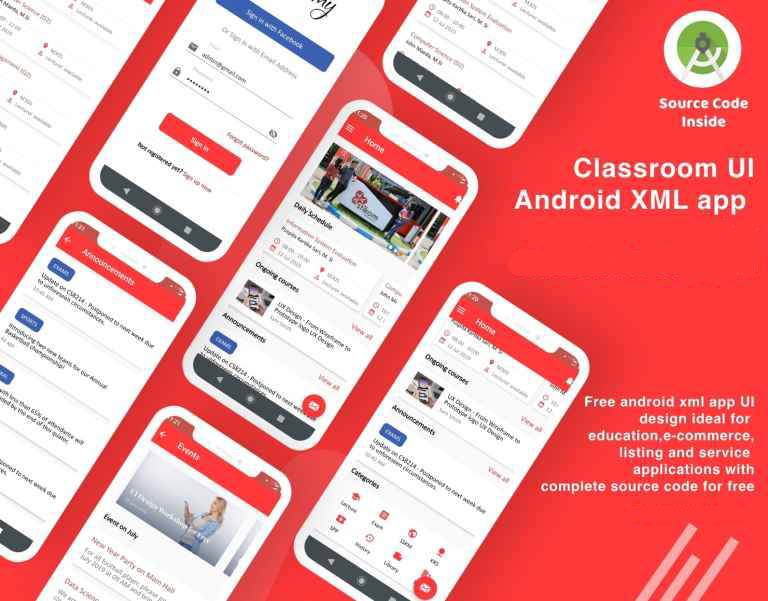
Here’s an example of an Android application that allows users to choose an image from the camera or gallery and perform cropping functionality using the “Android Image Cropper” library.
Step 1: Set up the project
Start by creating a new Android project in Android Studio. Make sure you have the necessary dependencies and permissions in your project’s build.gradle file:
dependencies {
implementation 'com.theartofdev.edmodo:android-image-cropper:2.8.+'
}Also, make sure you have the necessary permissions in your AndroidManifest.xml file:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />Step 2: Create the layout
Create a layout file called activity_main.xml with the following code:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingLeft="16dp"
android:paddingTop="16dp"
android:paddingRight="16dp"
android:paddingBottom="16dp"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:adjustViewBounds="true"
android:scaleType="centerInside"
android:src="@drawable/placeholder" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnChooseImage"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/imageView"
android:text="Choose Image" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnCropImage"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/btnChooseImage"
android:text="Crop Image"
android:enabled="false" />
</RelativeLayout>Step 3: Implement the functionality in the MainActivity
Open MainActivity.java and add the following code:
import android.Manifest;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.provider.MediaStore;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat;
import androidx.core.content.ContextCompat;
import com.theartofdev.edmodo.cropper.CropImage;
import com.theartofdev.edmodo.cropper.CropImageView;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final int REQUEST_CAMERA_PERMISSION = 200;
private static final int REQUEST_IMAGE_CAPTURE = 100;
private static final int REQUEST_IMAGE_GALLERY = 101;
private ImageView imageView;
private Button btnChooseImage;
private Button btnCropImage;
private Uri imageUri;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
imageView = findViewById(R.id.imageView);
btnChooseImage = findViewById(R.id.btnChooseImage);
btnCropImage = findViewById(R.id.btnCropImage);
btnChooseImage.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
chooseImage();
}
});
btnCropImage.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
cropImage(imageUri);
}
});
}
private void chooseImage() {
if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, Manifest.permission.CAMERA) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, new String[]{Manifest.permission.CAMERA}, REQUEST_CAMERA_PERMISSION);
} else {
openImageChooser();
}
}
private void openImageChooser() {
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_GET_CONTENT);
intent.setType("image/*");
startActivityForResult(intent, REQUEST_IMAGE_GALLERY);
}
private void cropImage(Uri imageUri) {
CropImage.activity(imageUri)
.setGuidelines(CropImageView.Guidelines.ON)
.setAspectRatio(1, 1)
.start(this);
}
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
if (requestCode == REQUEST_IMAGE_CAPTURE && resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
cropImage(imageUri);
} else if (requestCode == REQUEST_IMAGE_GALLERY && resultCode == RESULT_OK && data != null) {
try {
Bitmap bitmap = MediaStore.Images.Media.getBitmap(getContentResolver(), data.getData());
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
imageUri = data.getData();
btnCropImage.setEnabled(true);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else if (requestCode == CropImage.CROP_IMAGE_ACTIVITY_REQUEST_CODE) {
CropImage.ActivityResult result = CropImage.getActivityResult(data);
if (resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
Uri resultUri = result.getUri();
try {
Bitmap croppedBitmap = MediaStore.Images.Media.getBitmap(getContentResolver(), resultUri);
imageView.setImageBitmap(croppedBitmap);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else if (resultCode == CropImage.CROP_IMAGE_ACTIVITY_RESULT_ERROR_CODE) {
Exception error = result.getError();
error.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public void onRequestPermissionsResult(int requestCode, @NonNull String[] permissions, @NonNull int[] grantResults) {
super.onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults);
if (requestCode == REQUEST_CAMERA_PERMISSION && grantResults.length > 0 && grantResults[0] == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
openImageChooser();
}
}
}That’s it! Now you have an Android application that allows users to choose an image from the camera or gallery and perform cropping functionality. Remember to replace the placeholder image with an actual placeholder image of your choice.
Note: Don’t forget to add the necessary runtime permissions check in your code to handle permissions for accessing the camera and gallery.